Cable is an electrical device used to transmit power or communication signals. It is commonly used in construction, power engineering and other fields. During the cable selection process, people often encounter two common cables - VV cables and YJV cables. They have some obvious differences in structure, use and performance.
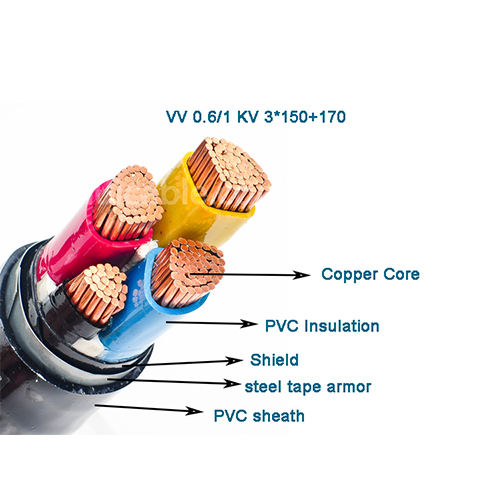
VV cable refers to PVC insulated and sheathed copper core power cable. The biggest advantages of VV cables are relatively low price, simple production process, and convenient and quick installation. VV cables are suitable for direct burial, power cable troughs, wire conduits and other environments, and are usually used at lower voltages. Its main components are conductor, insulation layer and sheath layer. YJV cable refers to a cross-linked polyethylene insulated and sheathed copper core power cable. YJV cable has relatively good performance in conductors and insulating materials, so it has stronger high temperature resistance and is suitable for power transmission in high temperature environments.
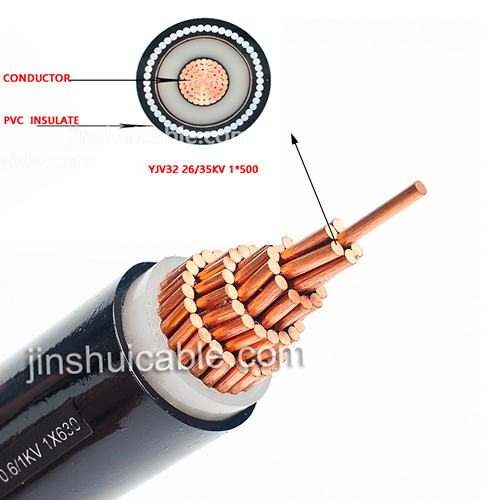
There are also differences in voltage levels between VV cables and YJV cables. VV cables are usually used in low-voltage power transmission and distribution systems, and their voltage levels are generally 0.6/1kV or below. YJV XLPE Power cables are also suitable for medium and low voltage transmission and distribution systems, but YJV wires and cables are mainly used in power systems with AC rated voltages of 6kV to 35kV, such as transmission lines, distribution lines, etc. Therefore, YJV cables have higher voltage transmission capabilities and are suitable for higher power power transmission.
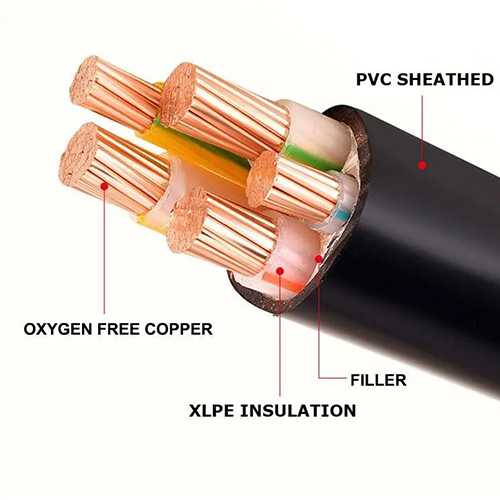
VV cables usually use copper core conductors, which have better electrical conductivity but higher costs. The conductor material of YJV cable can be copper core or aluminum core. Aluminum core is lighter and cheaper. In addition, the insulation material of YJV cable is cross-linked polyethylene. Compared with PVC insulated VV cable, it has better insulation performance and stronger voltage resistance.
In terms of comprehensive performance, YJV cable has better heat resistance and chemical corrosion resistance than VV cable. Because the insulation material of YJV cable is better, it can withstand higher temperatures, and the heat loss of the cable during operation is also lower. In addition, YJV cables also have advantages in chemical corrosion resistance, and have excellent electrical and mechanical properties, which can meet the normal operation in harsh environments such as high temperature, low temperature, humidity, and underwater, and can better resist acid and alkali corrosion and Factors such as humidity and corrosion. Therefore, YJV wires and cables are widely used in power systems.
To sum up, there are some significant differences between VV cables and YJV cables in terms of structure, use and performance. Choosing the right cable requires judgment based on specific needs to ensure the quality and safety of power transmission.
Get A Free Quote

The number of cable cores is selected based on comprehensive consideration of multiple factors to ensure the rational use of the cable.

Copper core cables have excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and good mechanical strength.

Wires are an important part of circuit reconstruction. Household wires are mainly divided into copper wires and aluminum wires.
Submit Request
PDF Request